[Amyloid and nucleic acid structure] The formation and propagation of meta-aggregates by RNA phase transition

Yasushi Yabuki
Department of Genomic Neurology, Institute of Molecular Embryology and Genetics (IMEG), Kumamoto University.
Assistant Professor
Institute of Molecular Embryology and Genetics, Kumamoto university.
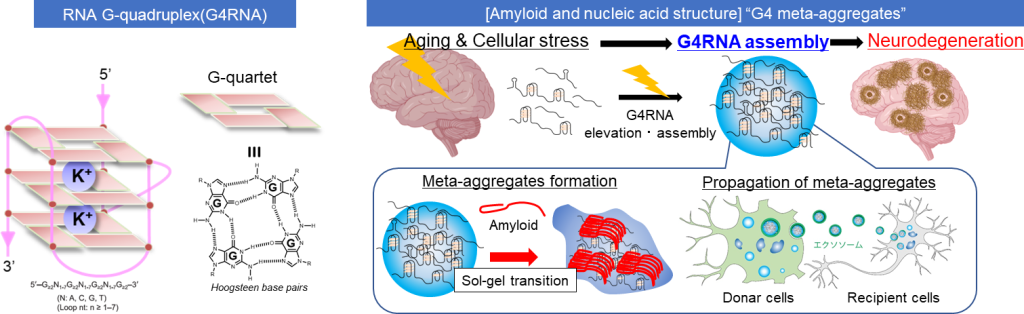
It is generally understood that DNA is a double helix structure and RNA is a single strand, however, DNA and RNA form a diverse secondary structure involved in the regulation of biological functions in cells. Especially, guanine-rich nucleic acids in DNA and RNA motifs can form non-canonical B-form structures called G-quadruplexes (G4). We have reported that RNA G-quadruplex (G4RNA) in guanine-rich repeat expansion promotes aggregation of FMRpolyG known as a prion-like protein associated with fragile X-related tremor/ataxia syndrome (FXTAS) (Sci Adv. 2021. 7(3):eabd9440.) and that G4RNA has an important role in stress granule formation in neurons (Sci Adv. 2023. 9(8):eade2035.). Moreover, we also demonstrated that G4RNA may be a key factor of amyloid formation involved in sporadic neurodegenerative disease (in preparation). Here, we aim to propose a novel concept that "G4 meta-aggregates" initiated by G4RNA are at the core of the development of neurodegenerative diseases.
- Research Collaborator Kazuya Matsuo
Department of Genomic Neurology, Institute of Molecular Embryology and Genetics (IMEG), Kumamoto University.
Assistant Professor - Research Collaborator Ginji Komiya
Department of Genomic Neurology, Institute of Molecular Embryology and Genetics (IMEG), Kumamoto University.
Graduate Student
